The Arndt–Eistert synthesis is a series of chemical reactions designed to convert a carboxylic acid to a higher carboxylic acid homologue (i.e. contains one additional carbon atom) and is considered ahomologation process. Named for the German chemists Fritz Arndt (1885–1969) and Bernd Eistert (1902–1978), Arndt–Eistert synthesis is a popular method of producing β-amino acids from α-amino acids. Acid chlorides react with diazomethane to give diazoketones. In the presence of a nucleophile (water) and a metal catalyst (Ag2O), diazoketones will form the desired acid homologue.
- In the Newman–Beal modification, addition of triethylamine to the diazomethane solution will avoid the formation of α-chloromethylketone side-products.
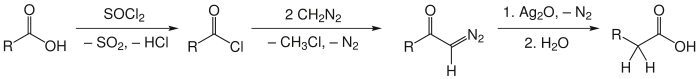
No comments:
Post a Comment