| Schem of the lipid bilayer on viruses, i.e. (Photo credit: Wikipedia) |
Lipid II is an amphipathic peptidoglycan precursor molecule involved in the synthesis of the cell wall of bacteria. The molecule is named for its bactoprenol hydrocarbon chain that acts as a lipid anchor, embedding itself in the bacterial cell membrane. The translocation of lipid II across the cell membrane is needed to incorporate its disaccharide-pentapeptide "building block" into peptidoglycan, making Lipid II the target of several antibiotics.
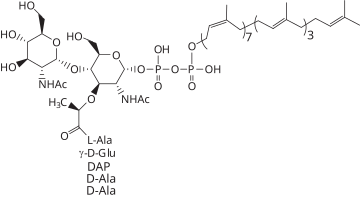 |
Antibiotics
Since Lipid II must be flipped outside the cytoplasmic membrane before incorporation of its disaccharide-peptide unit into peptidoglycan, it is a relatively accessible target for antibiotics. These antibiotics fight bacteria by either directly inhibiting the peptidoglycan synthesis, or by binding to lipid II to form destructive pores in the cytoplasmic membrane. Examples of antibiotics that target Lipid II include:
- Vancomycin and its synthetic derivatives
- Ramoplanin
- Several lantibiotics, including the common food preservative nisin
- Teixobactin
- Copsin
- Human alpha defensins
Binding
The D-Ala-D-Ala terminus is used by glycopeptide antibiotic vancomycin to inhibit lipid I- and lipid II-consuming peptidoglycan synthesis; in vancomycin-resistant strains vancomycin cannot bind, because a crucial hydrogen bond is lost. Oritavancin also uses the D-Ala-D-Ala terminus, but in addition it uses the crossbridge and D-iso-glutamine in position 2 of the lipid II stem peptide, as present in a number of Gram-positive pathogens, like staphylococci and enterococci. The increased binding of oritavancin through amidation of lipid II can compensate for the loss of a crucial hydrogen bond in vancomycin-resistant strains,








No comments:
Post a Comment