 |
| CHYMOSIN COMPLEX WITH THE INHIBITOR CP-113972 (Photo credit: Wikipedia) |
Chymosin /ˈkaɪməsᵻn/ or rennin /ˈrɛnᵻn/ is a protease found in rennet. It is an aspartic endopeptidase belongs to MEROPS A1 family. It is produced by newborn ruminant animals in the lining of the fourth stomach to curdle the milk they ingest, allowing a longer residence in the bowels and better absorption. It is widely used in the production of cheese. Bovine chymosin is now produced recombinantly in E. coli, Aspergillus niger var awamori, and K. lactis as alternative resource.
Recombinant Chymosin
Because of the imperfections and scarcity of microbial and animal rennets, producers sought replacements. With the development of genetic engineering, it became possible to extract rennet-producing genes from animal stomach and insert them into certainbacteria, fungi or yeasts to make them produce chymosin during fermentation. The genetically modified microorganism is killed after fermentation and chymosin is isolated from the fermentation broth, so that the fermentation-produced chymosin (FPC) used by cheese producers does not contain any GM component or ingredient. FPC contains the identical chymosin as the animal source, but produced in a more efficient way. FPC products have been on the market since 1990 and have been considered in the last 20 years the ideal milk-clotting enzyme.
FPC was the first artificially produced enzyme to be registered and allowed by the US Food and Drug Administration. In 1999, about 60% of US hard cheese was made with FPC and it has up to 80% of the global market share for rennet.
By 2008, approximately 80% to 90% of commercially made cheeses in the US and Britain were made using FPC. Today, the most widely used fermentation-produced chymosin is produced either by the fungus Aspergillus niger and commercialized under the trademark CHY-MAX® by the Danish company Chr. Hansen, or produced by Kluyveromyces lactis and commercialized under the trademark MAXIREN® by the Dutch company DSM.
FPC contains only chymosin B, achieving a high degree of purity compared with animal rennet. FPC can deliver several benefits to the cheese producer compared with animal or microbial rennet, such as higher production yield, better curd texture and reduced bitterness.
 |
| "Ostkaka" ("cheese cake"), traditional Swedish dish made of milk and cheese rennet. (Photo credit: Wikipedia) |
Rennet /ˈrɛnᵻt/ is a complex of enzymes produced in the stomachs of ruminant mammals. Chymosin, its key component, is a protease enzyme that curdles the casein in milk. This helps young mammals digest their mothers' milk. Rennet can also be used to separate milk into solid curds for cheesemaking and liquid whey. In addition to chymosin, rennet contains other important enzymes such as pepsin and a lipase.
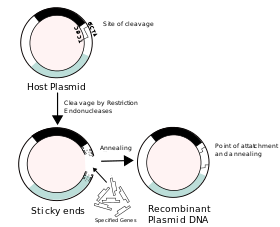


Kluyveromyces lactis is a Kluyveromyces yeast commonly used for genetic studies and industrial applications. Its name comes from the ability to assimilate lactose and convert it intolactic acid.


I was diagnosed as HEPATITIS B carrier in 2013 with fibrosis of the
ReplyDeleteliver already present. I started on antiviral medications which
reduced the viral load initially. After a couple of years the virus
became resistant. I started on HEPATITIS B Herbal treatment from
ULTIMATE LIFE CLINIC (www.ultimatelifeclinic.com) in March, 2020. Their
treatment totally reversed the virus. I did another blood test after
the 6 months long treatment and tested negative to the virus. Amazing
treatment! This treatment is a breakthrough for all HBV carriers.